¤ Structure of the nervous tissue
It is formed of two distinct cell types :
1\ Neurons Excitable cells initiate and transmit nerve impulses.
2\ Neuroglia cells Nonexcitable cells Support and protect the neurons.
¤ Neuron
*The neuron is the functional and structural unit of the central nervous system Characteristics of Neuron.
* Neurons have a high metabolic rate.
* Neurons have extreme longevity.
* Neurons typically are non-mitotic.
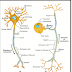
* Structure of neuron :
1- Cell body (soma, perikaryon).
2- Dendrites Axon Cell body (soma, perikaryon).3- Cell membrane It is very thin.
4- Nucleus Large Regular round or oval(vesicular) Situated fairly centrally.
5- Cytoplasm.
6- Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER) – Nissl’s bodies.
7- Golgi apparatus.
8- Mitochondria.
9- No centrioles Neurofibrils.
10- Glucogen Melanin pigments Lipofuscin granules, Fat droplets.
¤ Axon Single Uniform in diameter, Length of axons is variable:
* some reach up to 100 cm. Originate from a short pyramid-like structure called the axon hillock (Lacks Nissl’s granules).
* The plasma membrane of the axon is termed the axolemma.
*The cytoplasm of the axon is termed the axoplasm.
* Collaterals arise from the axon.
* Axon and collaterals end in fine processes called axon terminals.






No comments:
Post a Comment