Amino Acids
Functions
1.
Protein structure (monomer units of peptide chains of protein).
2.
Biosynthesis of:
n Nucleotides (Aspartate,Glutamine and Glycine).
n Glucose (glucogenic amino acids eg. Alanine).
n Histamine (Histidine).
n thyroxine (Tyrosine).
n Neurotransmiters
(Glutamate, Aspartate and Glycine)
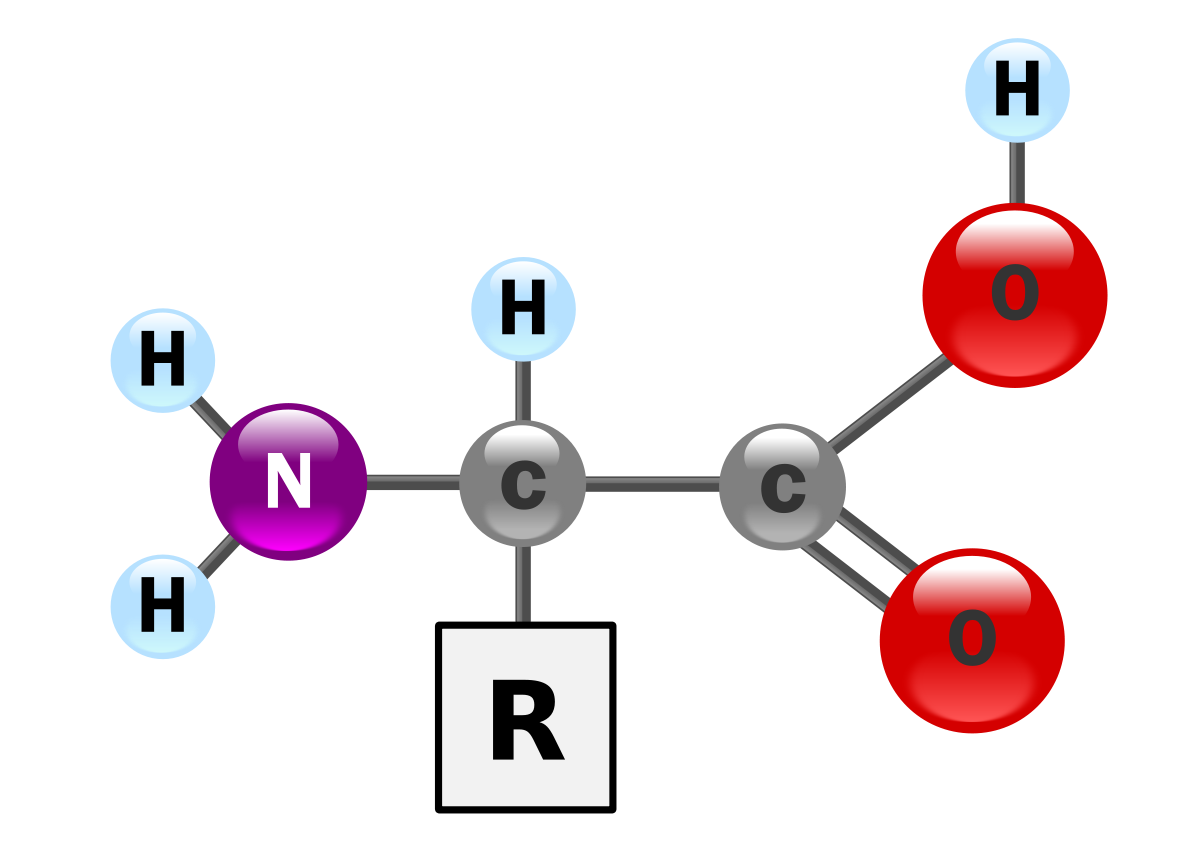
General Structure of Amino Acids :
n More than 300 amino acids found in
nature, but only 20 amino acids (These are the only amino acids that are coded
for by DNA) form proteins (the L-amino acids).
n Amino acids composed of an amino
group (NH2), a carboxyl group (-COOH) , a hydrogen atom and a distinctive side
chain, all bonded to an α-carbon
atom.
n The name of the different amino
acids have been given three letter and one letter abbreviation.
- Glycine , Alanine , Valine , Leucine , Isoleucine , Proline , Methionin , Cysteine , Phenylalanine , Tyrosine , Tryptophan , Arginine , Lysine , Histidine , Aspartate , Glutamate , Serine , Threonine , Asparagine , Glutamine
Characteristics of Amino Acids
n A symmetric carbons (except glycine).
n Enantiomers:
-
L-amino acids (incorporated into proteins)
- D-
amino acids (found in bacterial cell walls & in many peptide antibiotics).
n Amphoteric (zwitterion) properties:
n Have both basic and acidic groups.
n The isoelectric point (PI):
is the point at which the positive and negative charge of amino acids equal
zero.
n Water soluble (most amino acids).
n Colorless
(they don’t absorb visible light).
Classification of Amino Acids
n According to R group:
n aliphatic amino acids.
n Aromatic amino acids.
n Sulphur amino acids.
n Positively charged amino acids
(Basic aa).
n Negatively charged amino acids (Acidic
aa).
n Hydroxy amino acids.
n Imino acid.
n According to Polarity:
n Nonplar amino acids
n Polar amino acids
n According to its nutritional
essentiality.
n Essential amino acids.
n Non essential amino acids.
Classification
of amino acids according to R group:
Aliphatic R groups :
1. Glycine
2. Alanine
3. Valine
4. Leucine
5. Isoleucine
n Sulphur
amino acids:
1. Cysteine
2. Methionine
n Hydroxy
amino acids:
1. Serine
2. Threonine
n Imino
acid: Proline
Classification According to Polarity :
n Non polar amino acids:
1. alanine 2. valine 3. leucine 4. isoleucine
5. methionine 6. phenylalanine 7.tryptophan 8. tyrosine
9. proline.
n Polar amino acids (the rest of amino acids).
Classification According to Nutritional Essentiality :
n Essential
Amino Acids.
n Non
Essential Amino Acids.
Rare (uncommon) Amino Acids :
n 5-OH lysine & 4-OH proline
(found in plant cell wall proteins and in collagen protein).
n Methyllysine (found in myosin, a
contractive protein of muscles).
n γ-Carboxyglutamate (found in prothrombin, and
bone proteins).






No comments:
Post a Comment