Peptides
Importance :
n As
major hormones e.g.
insulin.n In
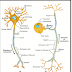
the nervous system as neurotransmitters or neuromodulators (e.g.
enkephalins).n Certain
antibiotics e.g. Bacitracin
and Polymyxin. enkephalin .
Formation :
- Peptide structure written from left to right starting from amino acid residue has free amino group (N-terminal)
- Peptides written using either three letter abbreviation e.g. ala, gly…. or one letter abbreviation (for long peptides).
- The peptide bond is formed between the α–carboxyl group of one amino acid and the α-amino group of another to form water.
- Peptide bonds formation require energy.
- The name tri peptide means have three amino acid residues (not three peptide bonds).
- The amino acid whose α-carboxyl group participated in the formation of peptide bond is termed amino acyl residue ( replace -ate or -ine by –yl e.g. alanyl, cysteinyl, tyrosine).
Characteristics
- Optically active (by component of amino acids).
- Amphoteric properties: Depends on the present of dissociating groups in the side chains and on the acidic or basic R group.
- Physiological Activity of Peptides
- Glutathione= Y-glutamyl-cystenyl-glycine: Is tripeptide. Have the y-glutamate (as an unusual amino acid). Important in redox reactions in the Red Blood Cells (RBCs).
- Vasopressin (VP), anti diuretic hormone (ADH): Is non a peptide.
- Function: in contraction of smooth muscles (increase the blood pressure), and re-absorption of H2O.
- Oxytocin: Non a peptide Hormone
- Function : contracts uterus (help delivery), and help release milk from lactating mammary glands.







No comments:
Post a Comment